Seasonal allergic rhinitis is a form of allergic rhinitis that occurs seasonally, typically in spring or autumn, and is associated with plant pollen. This common upper respiratory condition is characterized by inflammation of the nasal mucous membrane upon contact with allergens, in this case, pollen. The impact of pollen on sensitive organisms triggers an allergic reaction, manifesting with various symptoms.
Causes and Development Mechanism
Seasonal allergic rhinitis is usually triggered by contact with plant pollen, such as trees, grasses, and flowers. When pollen enters the body through the respiratory tract or mucous membranes of susceptible individuals, the immune system reacts by producing IgE antibodies. Upon subsequent contact with the same type of pollen, IgE antibodies bind to mast cells, causing their degranulation and release of chemical substances, such as histamine, which triggers inflammation of the nasal mucous membrane.
Symptoms
Symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis may include:
- Sneezing: Frequent or persistent sneezing, especially upon contact with pollen.
- Runny Nose: Continuous secretion of transparent or cloudy mucus from the nose.
- Nasal Itching and Irritation: Sensation of itching, burning, or irritation in the nose.
- Nasal Congestion: Feeling of stuffiness or difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Red and Itchy Eyes: Inflammation of the eye’s conjunctiva, accompanied by redness, itching, and tearing.
- Fatigue: Prolonged disruption of sleep due to rhinitis symptoms can lead to fatigue and irritability.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of seasonal allergic rhinitis typically relies on clinical symptoms, medical examination, and patient history. Additional methods, such as skin allergy tests or blood tests for IgE antibodies, may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment and Management
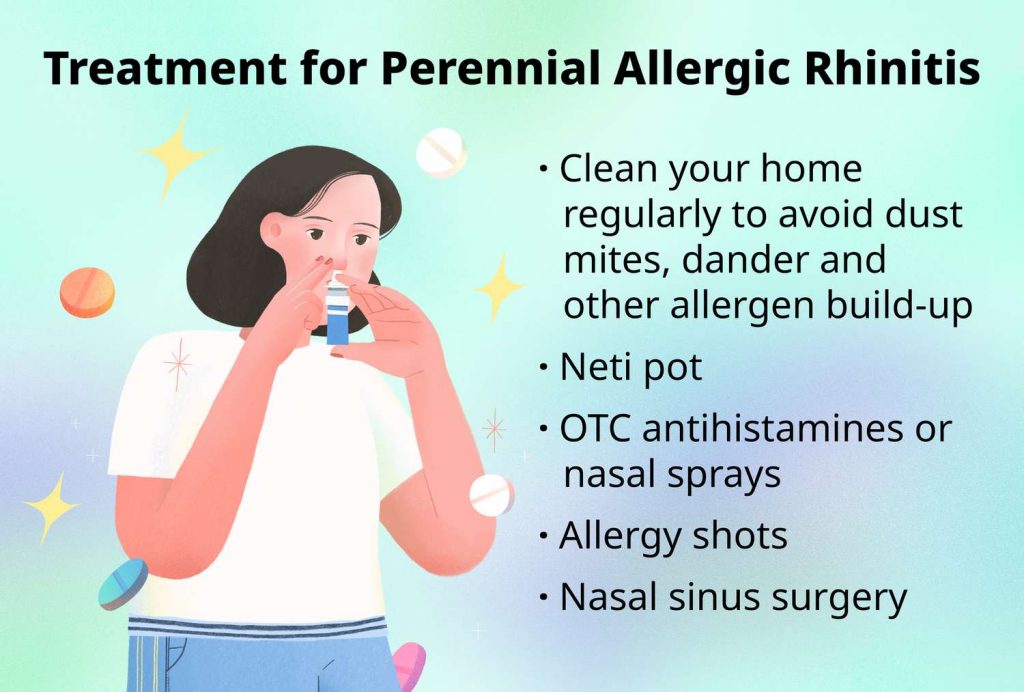
Treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis aims to alleviate symptoms and prevent their recurrence. It may include:
- Use of Antihistamine Medications: To reduce itching and mucus secretion from the nose.
- Utilization of Glucocorticoid Nasal Sprays: To reduce inflammation of the nasal mucous membrane.
- Avoidance of Pollen Exposure: By limiting outdoor activities during periods of high pollen levels.
- Immunotherapy: In some cases, immunotherapy may be recommended to reduce sensitivity to pollen.
Prevention
Prevention of seasonal allergic rhinitis involves measures to avoid contact with pollen, such as wearing masks or protective gear, avoiding outdoor activities during high pollen periods, and regular home cleaning to reduce allergen levels indoors.
Seasonal allergic rhinitis can significantly impact quality of life, but proper symptom management and preventive measures can substantially alleviate the condition and improve patient comfort.