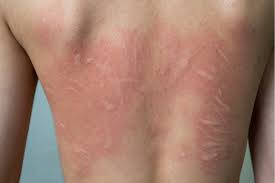
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a type of allergic skin reaction characterized by the appearance of itchy, raised, reddish patches or welts resembling the sting of a nettle. This reaction is usually associated with contact with allergens that trigger sensitivity in individuals. Hives may appear within minutes to hours after contact with the allergen and typically disappear within 24 hours. However, they may sometimes persist for a longer period or recur periodically.
The causes of hives can vary from person to person and include:
- Allergens: Pollen, food items (such as nuts, dairy products, eggs), medications (e.g., antibiotics, aspirin), animals, and many other substances can trigger an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals.
- Physical irritants: For example, cold, sunlight, pressure on the skin, friction.
- Immunological causes: Some cases of hives may be associated with immune system disorders.
Symptoms of hives may include:
- Itchy, raised red patches on the skin.
- Individual patches or clusters of patches on the skin.
- Redness and swelling of the affected area.
- Heat or burning sensation in the affected area.
- Rarely: swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing, angioedema.
The diagnosis of hives is often based on clinical symptoms and medical history. In cases where the cause is not obvious, allergic testing or other diagnostic methods may be required.
Treatment of hives includes:
- Avoiding known allergens or irritants, if identified.
- Using antihistamine medications to relieve itching and reduce the reaction.
- Applying corticosteroid creams or ointments to reduce inflammation and itching.
- In cases of severe hives that do not respond to standard treatment, immunomodulators or other medications may be used.
- In cases of allergic hives that pose a life-threatening risk (anaphylactic shock), immediate medical assistance may be required.
It is important to note that hives are usually a temporary and easily manageable condition, but in some cases, they may persist for a long time or become chronic. If you experience symptoms of hives, consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.